What are Semantic Elements?
A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer.
Examples of non-semantic elements: <div> and <span> - Tells nothing about its content.
Examples of semantic elements: <form>, <table>, and <article> - Clearly defines its content.
Semantic Elements in HTML
Many web sites contain HTML code like: <div id="nav"> <div class="header"> <div id="footer"> to indicate navigation, header, and footer.
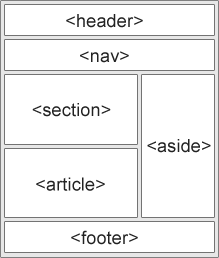
In HTML there are some semantic elements that can be used to define different parts of a web page:
- <article>
- <aside>
- <details>
- <figcaption>
- <figure>
- <footer>
- <header>
- <main>
- <mark>
- <nav>
- <section>
- <summary>
- <time>
HTML <section> Element
The <section> element defines a section in a document.
According to W3C's HTML documentation: "A section is a thematic grouping of content, typically with a heading."
Examples of where a <section> element can be used:
- Chapters
- Introduction
- News items
- Contact information
A web page could normally be split into sections for introduction, content, and contact information.
| Live Demo & Try it yourself! | Read More » » |

